Understanding Diabetes: Causes, Symptoms, and Management
Understanding Diabetes: Causes, Symptoms, and Management
Written by Muhammad Nadeem KhanTypes of Diabetes
1. Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes, previously known as juvenile diabetes or insulin-dependent diabetes, typically manifests in childhood or adolescence. This form of diabetes occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. Consequently, the body is unable to produce insulin, leading to unregulated blood sugar levels.
2. Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes, the most common form of diabetes, primarily develops in adults, although it is increasingly diagnosed in children and adolescents due to rising obesity rates. In type 2 diabetes, the body either becomes resistant to insulin or fails to produce enough insulin to meet its needs. Lifestyle factors such as poor diet, sedentary behavior, and obesity significantly contribute to the development of type 2 diabetes.
3. Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes occurs during pregnancy when hormonal changes impair insulin action, resulting in elevated blood sugar levels. While gestational diabetes typically resolves after childbirth, it increases the risk of both the mother and child developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
Other Forms of Diabetes
Causes and Risk Factors
Genetic Predisposition
Genetics plays a significant role in the development of diabetes, particularly type 1 diabetes, where individuals with a family history of the condition are at higher risk.
Lifestyle Factors
Gestational Factors
During pregnancy, hormonal changes can predispose some women to develop gestational diabetes, especially if they are overweight or have a family history of diabetes.
Autoimmune Response
In type 1 diabetes, an autoimmune response triggers the destruction of insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas, leading to insulin deficiency.
Symptoms
- Excessive thirst and hunger
- Frequent urination
- Fatigue
- Unexplained weight loss (in type 1 diabetes)
- Blurred vision
- Slow-healing wounds
- Tingling or numbness in the hands and feet
Diagnosis
Blood Tests
Glycated Hemoglobin (HbA1c)
The HbA1c test measures the average blood sugar level over the past two to three months and is considered a reliable indicator of long-term blood glucose control.
Random Blood Sugar Test
Treatment and Management
Lifestyle Modifications
- Following a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins
- Regular physical activity to improve insulin sensitivity and regulate blood sugar levels
- Maintaining a healthy weight through calorie control and portion management
Medications
For individuals with type 1 diabetes, insulin therapy is essential to replace the hormone the body cannot produce. In type 2 diabetes, oral medications, injectable therapies, or insulin may be prescribed to lower blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity.
Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels
Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels through self-testing and periodic medical evaluations is crucial for managing diabetes effectively.
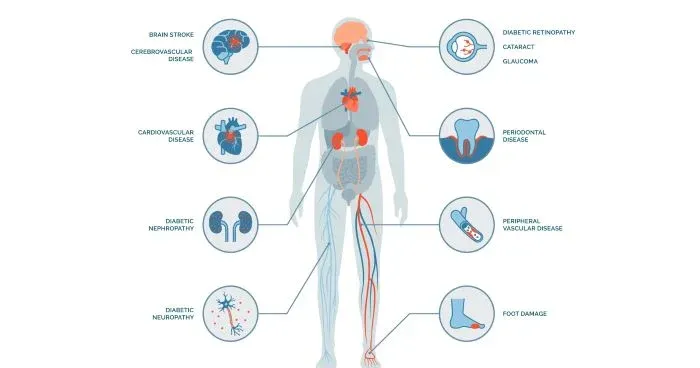
Complication Prevention
Proper diabetes management aims to prevent or delay the onset of complications such as cardiovascular disease, kidney disease, nerve damage, and vision problems.
Prevention
Healthy Eating Habits
Adopting a well-balanced diet low in refined sugars and saturated fats and high in fiber, fruits, and vegetables can help prevent type 2 diabetes and manage blood sugar levels.
Regular Exercise
Weight Management
Regular Medical Check-ups
For the Complete and Detailed Article: Click HERE
References
1. World Health Organization (WHO). (n.d.). Diabetes.
https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/diabetes
2. Cleveland Clinic. (n.d.). Diabetes.
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/7104-diabetes
3. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). (n.d.). Diabetes. https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/basics/diabetes.html
4. Mayo Clinic. (n.d.). Diabetes.
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/diabetes/symptoms-causes/syc-20371444
Disclaimer Note:
The information provided in this article is intended for educational and awareness purposes only.
It is highly recommended to consult with a qualified healthcare provider or physician before making any decisions regarding your health or medical care.
We do not take responsibility for any adverse effects, complications, or outcomes resulting from the implementation of the information provided in this article. Each individual's health condition is unique, and what works for one person may not work for another.






Comments
Post a Comment